Table of contents
- Key Takeaways
- Defining the Value Chain Industry
- Key Components of a Value Chain
- The Role of Value Chain Analysis
- How Value Chains Drive Competitive Advantage
- Global Value Chains
- Technology’s Impact on the Value Chain Industry
- Virtual Value Chains
- Practical Examples of Value Chains
- Steps to Conducting a Value Chain Analysis
- Value Chain vs. Supply Chain
- Future Trends in the Value Chain Industry
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Links
This article explores the elements and benefits of value chains, including all the stages a company goes through to produce and deliver a product. Understanding these steps is essential for businesses to stay competitive and improve their operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
-
The value chain is a series of activities that companies perform to deliver a product or service, aiming to enhance product value and reduce costs.
-
Primary activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, while support activities enhance the efficiency of these processes.
-
Conducting a value chain analysis allows businesses to identify inefficiencies, streamline operations, and enhance profitability, ultimately leading to a competitive advantage.
Defining the Value Chain
The value chain is all the activities involved in making a product or service, from getting raw materials to delivering the final product. It shows how a company turns inputs into outputs in its production process. By looking closely at the value chain, companies can focus on specific stages for detailed analysis and opportunities for improvement.
Michael Porter identifies two types of activities in the value chain: primary and secondary. Primary activities are inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service provision. Support activities include firm infrastructure management, human resource management practices, technological development strategies implemented by firms within their sector-specific context, and procurement processes. This structure aims to improve product or service quality while reducing costs. Maximizing efficiency at reduced expenses is vital for gaining a competitive advantage.
Analyzing each step in this process helps companies find ways to spend less and add more value, giving them a competitive edge. Organizations can improve operations by comparing the costs at each stage with the value they add to the final product, leading to reduced costs and increased profits. As products move through this process, they gain more value, showing the importance of each stage in production.
Key Components of a Value Chain
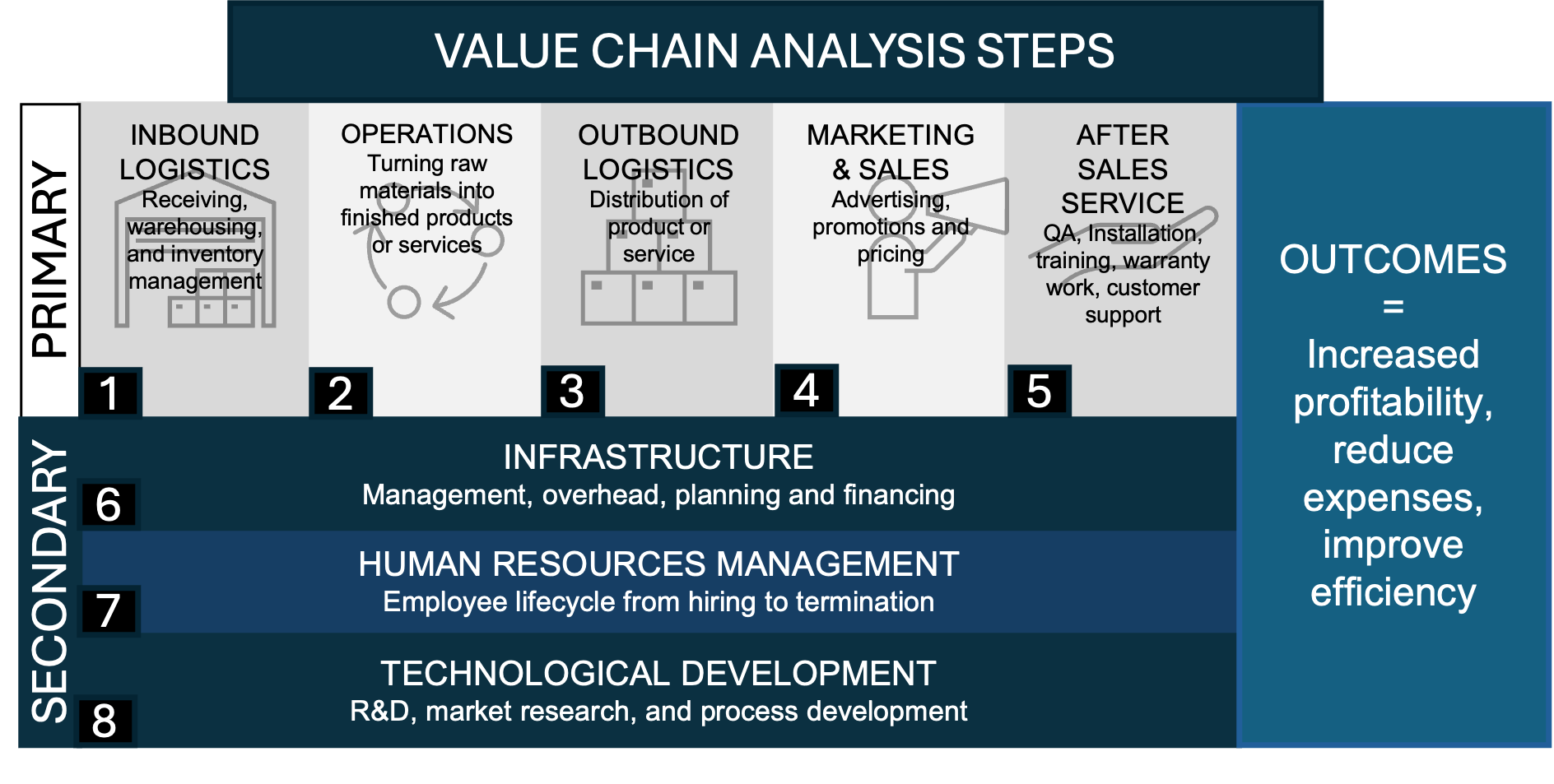
Value Chain Analysis
A value chain is made up of many connected links, each of which contributes to adding value and creating a complex network of activities. These components are divided into primary activities, which involve producing goods or services directly, and support activities that improve the productivity of these processes. Together, they improve efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately boosting performance and providing a competitive advantage.
A well-designed value chain ensures that all activities within it are in line with the company’s strategic goals. Understanding how primary and support activities interact helps companies stay competitive in the market and improve their operations for better long-term performance.
Primary Activities
The value chain includes important activities like getting and handling raw materials and ensuring they are available for making products. The part of the value chain that deals with making products involves turning these raw materials into the final product by effectively managing labor and equipment.
The next step is getting the finished product to customers. This includes managing inventory and sending out orders. Marketing and sales are important for making people aware of the product and bringing in money. After the sale, providing services like installation and repairs is essential for keeping customers happy and loyal to the brand.
The value chain is important for businesses because it involves turning raw materials into finished products, improving distribution, and providing support after a sale. This network is crucial for business success and making a profit by creating high-quality products from the beginning materials.
Support Activities
Support activities play a significant role in improving the primary activities in a value chain. The firm’s infrastructure, including its management and organizational structure, helps with decision-making and strategy execution. Human resource management focuses on attracting, developing, and retaining an effective workforce that supports company objectives.
Obtaining resources for both primary and secondary parts of the value chain is a key procurement task. This involves acquiring the materials needed for manufacturing, negotiating with suppliers effectively, and maintaining good relationships to ensure high-quality control at cost-effective levels. Managing costs through support activities is essential for driving better overall performance across the value chain.
To thrive, businesses must smoothly integrate support with their core functions throughout their value chain. This integration is crucial for positioning these companies advantageously for long-term success.
How Value Chains Drive Competitive Advantage
Grasping the intricacies of value chains allows organizations to pinpoint potential areas for increasing both cost-effectiveness and customer and stakeholder value. Conducting a thorough chain analysis can reveal paths toward obtaining a competitive advantage by boosting productivity and elevating customer satisfaction. The value chain framework suggests that two primary strategies, namely differentiation and cost leadership within the context of the chain concept, are essential for gaining a competitive edge.
Enhancements in processes throughout the value chain are key to improving customer satisfaction levels. By understanding how customers perceive value, companies can refine their product or service offerings accordingly. For instance, Trader Joe’s demonstrates successful management of its value chains through outstanding consumer care paired with distinctive marketing approaches—a testament to achieving a substantial competitive edge via effective operation along these chains.
Combining support activities with core functions can help reduce costs and improve product quality. Using virtual value chains is important because they improve information flow and teamwork, giving companies a competitive edge by helping them adapt quickly to market changes.
Global Value Chains
Often, a value chain encompasses multiple stakeholders scattered across various locations, frequently mirroring a global configuration. Multinational companies play an integral role in orchestrating these global value chains via their overseas activities. These international value chains entail dividing production processes among different countries to maximize efficiency and minimize costs without compromising product quality. Think of the production of a vehicle where materials and components can be sourced and produced all over the world and shipped to a final destination for vehicle assembly.
These worldwide value chains promote cooperative efforts between diverse nations and areas, fostering economic interconnectivity.
Technology’s Impact on the Value Chain
Technological advancements, including automation and data analytics, create more adaptive and efficient value chain systems. Technology development includes research and improvements that enhance the efficiency of both primary and support activities. Utilizing AI and Big Data can enable brands to integrate their operations throughout the value chain, enhancing efficiency and profitability.
Digitally integrated value chain solutions can lead to significant improvements, such as a 50% increase in market response speed and a reduction in manufacturing costs by up to 20%. Industries like fashion are increasingly adopting custom technology solutions to overcome the lack of comprehensive off-the-shelf options for end-to-end value chain integration.
Trader Joe’s unique system for receiving and shelving products during store hours is another example of effective technology use to maximize efficiency and cost savings.
Practical Examples of Value Chains
Case studies illustrate that effective value chain management can lead to significant competitive advantages for companies. For instance, 2pure increased its revenue by 95% through value chain improvements. Trader Joe’s has also successfully implemented value chain strategies to enhance its market position.
Demonstrating these value chain examples shows the importance of thorough value chain analysis for any organization aiming for operational success. Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how companies can leverage their value chains to achieve substantial business growth and competitive advantage.
Steps to Conducting a Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis evaluates individual business operations to bolster production efficiency and reduce expenses. The first phase involves pinpointing every step required to create the final product and evaluating the cost tied to each step. Continual examination of the value chain enables businesses to detect areas where efficiency is lacking, thus fostering an increase in profit margins.
After recognizing these activities within the chain, assessing their costs and contributions can reveal which aspects are most financially demanding and ripe for enhancement. By scrutinizing whether the outcome justifies its expense regarding resources expended—such as money, time, or labor—companies have an opportunity to refine their performance across various segments of their operations through strategic action.
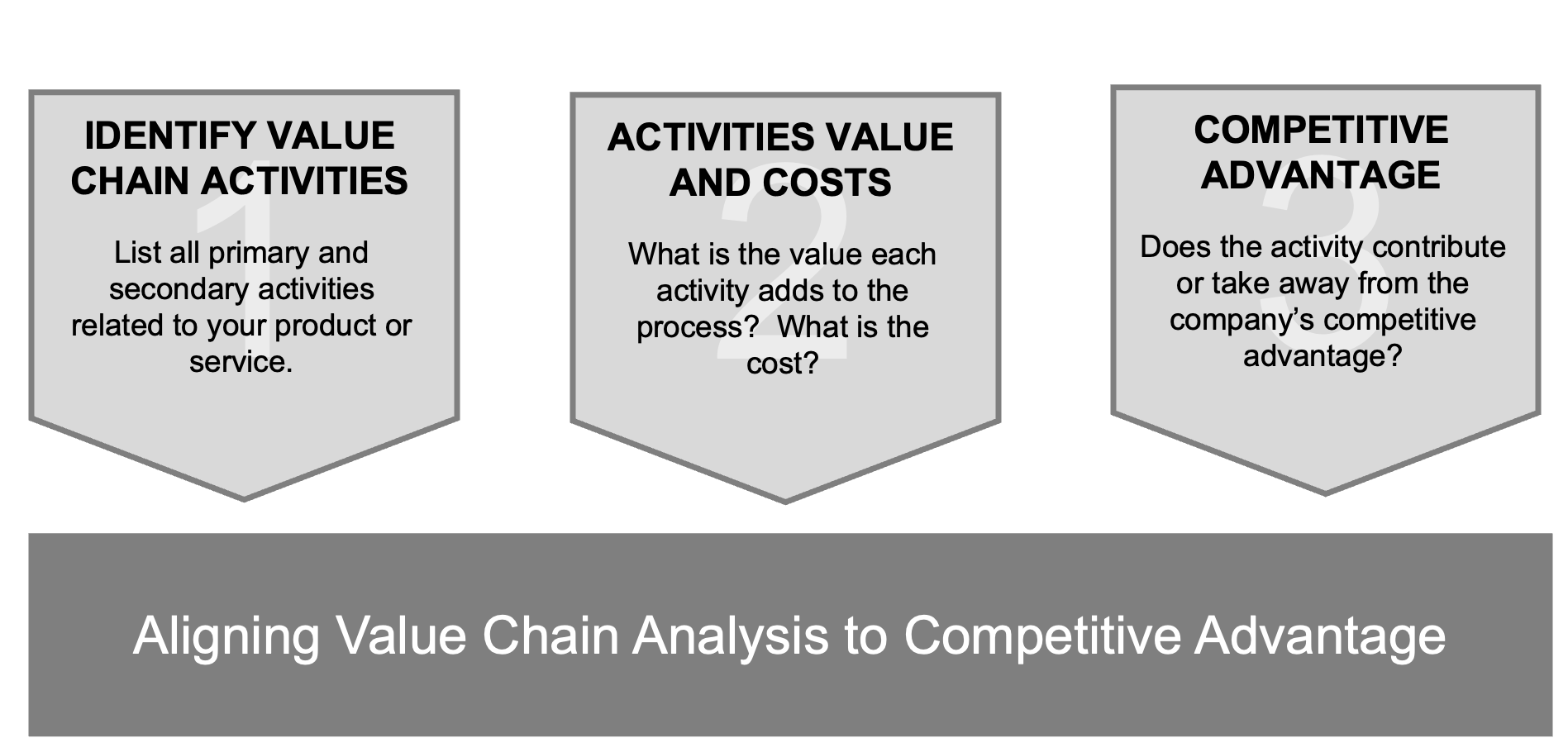
3 Step Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain vs. Supply Chain
The value chain focuses on increasing a product’s value, while the supply chain focuses on improving production and distribution processes. Supply chains primarily deal with logistics, while value chains integrate logistics with strategic business management practices. Both chains aim to increase profits, with value chains focusing on gaining a competitive edge through product improvement, and supply chains prioritizing operational efficiency.
Both supply chain management and value chain management involve logistic functions, but they have different goals. Supply chain management aims for efficiency, while value chain management focuses on enhancing customer-perceived value. Understanding these distinct aims helps businesses improve their overall performance and success.
Summary
In this blog post, we’ve examined how value chains work, what they’re made of, why it’s important to study them, and how technology affects them. Understanding and improving your value chain is crucial to staying competitive in today’s fast-paced business world.
Looking forward, sustainability and technological advancements will influence value chains in the future. Businesses can use these trends to improve their operations, cut costs, and provide more value to their customers. Keep these insights in mind when dealing with the complex world of value chains, and you’ll be on the path to success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a value chain?
The fundamental goal of a value chain is to increase the value of products while reducing expenses, thus delivering maximum value and securing a competitive advantage.
How does value chain analysis help businesses?
By undertaking value chain analysis, companies can pinpoint areas ripe for refinement within their operations, thus optimizing the creation of value while simultaneously reducing expenses to maintain a competitive advantage.
Employing this systematic method allows firms to bolster both effectiveness and earnings.
What are the key differences between a value chain and a supply chain?
The essential contrast lies in the fact that a value chain accentuates amplifying the value of products through strategic procedures, whereas a supply chain concentrates on optimizing the production and distribution efficiency for merchandise.
Recognizing this differentiation is vital for proficient business administration.
How do global value chains benefit companies?
Companies gain a competitive advantage through global value chains by strategically dividing production tasks among various countries to increase efficiency, lower manufacturing expenses, and uphold the quality of their products.
This method enables firms to exploit worldwide resources and competencies in an efficient manner.


